Welcoming a new baby is an exciting time, but it can also come with concerns.
One common condition that affects many newborns is jaundice. Let’s explore what jaundice is, why it occurs, and how it’s treated.
What is Newborn Jaundice?
Jaundice is a yellowing of a baby’s skin and eyes.
It’s incredibly common, affecting about 60% of newborns.
This condition is caused by a buildup of bilirubin in the baby’s blood and tissues.
Why Does It Happen?
Newborns have a high number of red blood cells, which are broken down frequently. This process produces bilirubin.
A newborn’s liver isn’t fully developed yet, so it can’t process bilirubin as effectively as an adult’s liver. This leads to a temporary buildup of bilirubin, causing the yellowing we see as jaundice.
Types of Jaundice
There are several types of jaundice in newborns:
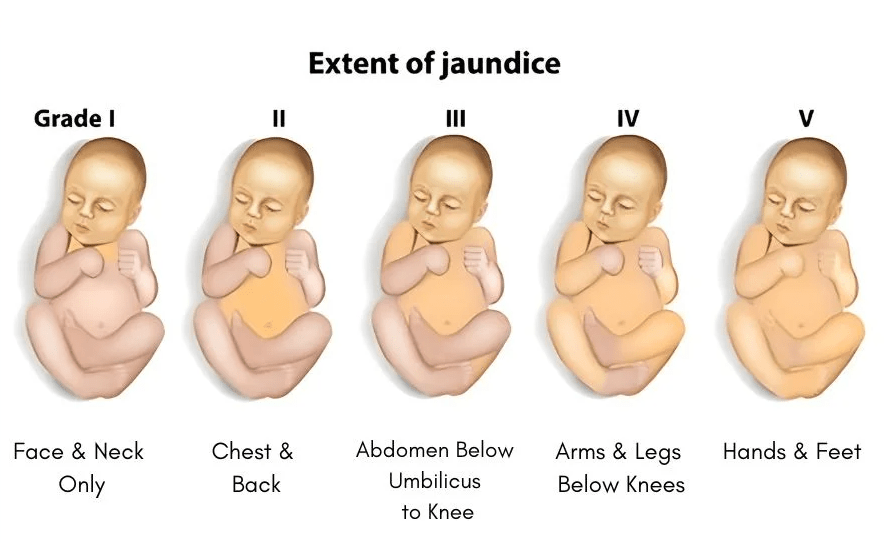
- Physiological jaundice: The most common type, usually appearing 2-3 days after birth.
- Breastfeeding jaundice: Occurs in the first week of life, often due to insufficient milk intake.
- Breast milk jaundice: May appear after the first week and can last for several weeks.
Treatment Options
For most babies, jaundice is mild and resolves on its own within 2-3 weeks.
However, for moderate to severe cases, treatments may include:
- Enhanced nutrition: More frequent feeding to prevent weight loss.
- Phototherapy: Exposing the baby to special blue lights that help break down bilirubin.
- In rare, severe cases: Intravenous immunoglobulin or exchange transfusion.
Home Care Tips
If your baby has mild jaundice, you can help by:
- Feeding frequently to encourage bowel movements, which help excrete bilirubin.
- Ensuring your baby gets enough fluids to prevent dehydration.
Remember, while jaundice is common, it’s important to have your baby checked by a healthcare provider to ensure proper treatment if needed.




댓글 남기기